From the EU to China: Understanding the Additional Steps for Cosmetics Regulatory Compliance
Expanding your business to new markets can be a great way to grow your brand and increase revenue. However, selling products in different regions often requires additional steps to ensure regulatory compliance. If you’re already selling cosmetics that comply with EU regulations and are looking to expand to the Chinese market, you may be wondering what extra steps you need to take to ensure compliance. This article will explore the key considerations and steps you need to take to ensure your products meet regulatory requirements in China.
What’s the difference between general cosmetics and special use cosmetics?
In contrast to the EU’s unified regulatory framework for cosmetics, China classifies cosmetics into two categories: general cosmetics and special cosmetics. Special cosmetics include products that claim to have specific effects such as hair dye, hair perm, anti-hair loss, sunscreen, spot-removing, and whitening. All other cosmetic products are considered general cosmetics. Special cosmetics require registration, while general cosmetics require notification. Registering special cosmetics involves a more comprehensive set of documents and tests compared to the notification process for general cosmetics. Consequently, the regulatory procedure for special cosmetics is more time-consuming and expensive.
Does China require animal testing on cosmetics after 2021?
Previously, all cosmetic products entering the Chinese market were required to undergo animal testing. However, with the implementation of the Measures on the Administration of Registration and Notification Dossier of Cosmetics in May 2021, animal testing can now be exempted under specific conditions.
Table 1 – Conditions for Animal Exemption in China
| Conditions | |
| A | It is general cosmetics. |
| B | Manufacturers have obtained a certificate issued by the government to prove their qualification to produce qualified products, such as Good Manufacturing Practices. |
| C | The safety assessment results can substantiate the safety of products. |
| D | It does not involve New Cosmetic Ingredients. |
| E | It is not intended for kids or infants. |
| F | Domestic responsible persons, notifiers, and manufacturers of products have no bad records in China. |
As for cosmetic products that can not be exempted from animal testing, some alternative testing methods can be adopted to substantiate the safety of cosmetics.
Table 2 – Alternatives to animal testing permitted in China
| Testing | Application Field | Testing Purpose | Does it involve animals? |
In vitro 3T3 NRU phototoxicity test | Cosmetic ingredients | To assess the phototoxicity of cosmetic ingredients | No |
Short Time Exposure In Vitro Test Method (STE) | Cosmetic ingredients | To assess the eye irritation of cosmetic ingredients | No |
| In Chemico Skin Sensitisation: Direct Peptide Reactivity Assay (DPRA) | Cosmetic ingredients | To assess the skin sensitization of cosmetic ingredients | No |
Bacterial Reverse Mutation Assay | Cosmetic ingredients or products | To assess the gene mutation of Cosmetic ingredients or products | No |
In Vitro Mammalian Cells Chromosome Aberration Test | Cosmetic ingredients or products | To assess the mutagenicity of Cosmetic ingredients or products | No |
In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Test | Cosmetic ingredients or products | To assess the mutagenicity of Cosmetic ingredients or products | No |
In Vitro Mammalian Cells Micronucleus Test | Cosmetic ingredients or products | To assess the mutagenicity of Cosmetic ingredients or products | No |
Are there any restrictions on exporting cosmetics from the EU to China?
In the EU, all cosmetic products are regulated by EU Regulation 1223/2009. This regulation includes a list of prohibited substances (Annex II) and substances subject to restrictions (Annex III). Similarly, China has its own Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics, which specify the permitted, prohibited, and conditionally permitted ingredients. However, these lists may not align completely with the EU regulations. It means that certain ingredients allowed in the EU may be prohibited in China, and vice versa. Additionally, there may be variations in restrictions, such as maximum concentrations. To ensure compliance with Chinese regulations, it is recommended to consult the lists of ingredients in the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics before introducing your products to the market.

Which additional documentation is required to export cosmetics from the EU to China?
As shown in Table 3, it is evident that the EU and China have different document requirements. However, the core elements of these documents are similar. They include general company and product information, manufacturer qualifications, safety and efficacy substantiation, compliant packaging and labelling, and more. Nevertheless, these documents must be compiled in accordance with Chinese requirements and presented in Chinese.
In addition, several documents need to be prepared prior to exporting products to China. These documents include the certificate of free sale, power of attorney, product specification standards, a summary of the adverse event monitoring system, a summary of the quality management system, product classification code, and Chinese labelling, among others.
All documents must be submitted in Chinese. Some documents, such as GMP, Certificate of Free Sale, and power of attorney, require the submission of the original documents translated into Chinese and attached alongside the originals.
It is important to note that standard Chinese characters should be used, with the exception of registered trademarks, website addresses, patent names, names and addresses of overseas companies, or commonly used professional terms (such as SPF, PFA, PA, UVA, UVB, vitamin C, etc.).
Table 3 – Mandatory Documents Required in the EU and China for Cosmetics Compliance
| Type of Document | EU | China |
|---|---|---|
| General Part | ||
Company information form | ✔ | ✔ |
Product Information and formula | ✔ | ✔ |
GMP certificate | ✔ | ✔ |
Method of manufacture | ✔ | ✔ |
| Samples | ✔ | ✔ |
Product classification code | ✔ | |
Power of attorney (original document) | ✔ | |
Certificate of Free Sale (original document) | ✔ | |
Summary of adverse event monitory system | ✔ | |
Summary of the quality management system and resume of the person in charge of safety and quality | ✔ | |
Raw Material Part | ||
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) of raw material | ✔ | |
Certificate of Analysis (COA) of raw material | ✔ | |
Non-animal testing Statement | ✔ | |
IFRA certificate and allergen report for fragrances and natural oils | ✔ | |
Finished Product Part | ||
Challenge test result | ✔ | |
Stability and compatibility test result | ✔ | |
MSDS/COA of finished product | ✔ | |
Non-animal testing statement | ✔ | |
Undesirable effect statement | ✔ | |
Safety assessment report and safety assessor resume | ✔ | ✔ |
Product specification standards | ✔ | |
Substantiation of the efficacy claims (if any) through tests or scientific literature/data | ✔ | ✔ |
Data on CMR, heavy metals, impurities and GMOs | ✔ | |
| Packaging and Labeling Part | ||
Packaging info | ✔ | ✔ |
| Product labeling | ✔ | ✔ |
Packaging declaration | ✔ |

What additional testing is required to export cosmetics from the EU to China?
When introducing products into the Chinese market, it is generally required to provide substantiation to prove the safety and efficacy of the products.
Safety testing includes microbiological testing, physicochemical testing, toxicity testing (which may involve animal testing in China), and safety testing on humans. It is important to note that different products may require different types of testing. In other words, your specific products may only need a subset of the aforementioned tests. However, all safety-related testing must be conducted in China and comply with the country’s set standards.
Regarding efficacy testing, some reports from tests conducted outside of China may be accepted, particularly for efficacy claims related to moisturizing, soothing, anti-dandruff, etc. However, according to the Standard for the Evaluation of Cosmetics Efficacy Claims, for cosmetics with claims of freckle-removing, whitening, sun protection, and anti-hair loss effects, efficacy evaluation tests on humans must be conducted in China in accordance with mandatory national standards and technical specifications. A report based on these tests is required. Therefore, efficacy testing for these specific claims must be performed in China.
If you require further information on which tests are required for your products, then consult this article Cosmetics Testing Required for Registration and Notification in China.
What are the labelling requirements for imported cosmetics in China?
According to the Cosmetics Supervision and Administration Regulation and Measures for the Administration of Cosmetics Labelling in China, cosmetic products intended for the Chinese market must have labels in Chinese. The labels should use standard Chinese characters. If other words or symbols are used, an explanation in standard Chinese characters should be provided on the same visible surface of the product.
If the registered trademark of the product uses letters, Chinese pinyin, numbers, symbols, or other non-Chinese characters, its meaning must be explained on the same visual surface.
With the exception of registered trademarks, the font size of other characters on the Chinese label should be smaller than or equal to the font size of the corresponding standardised Chinese characters.
In cases where a Chinese label is affixed to the original packaging in a foreign language, the Chinese label must adhere to the aforementioned requirements.

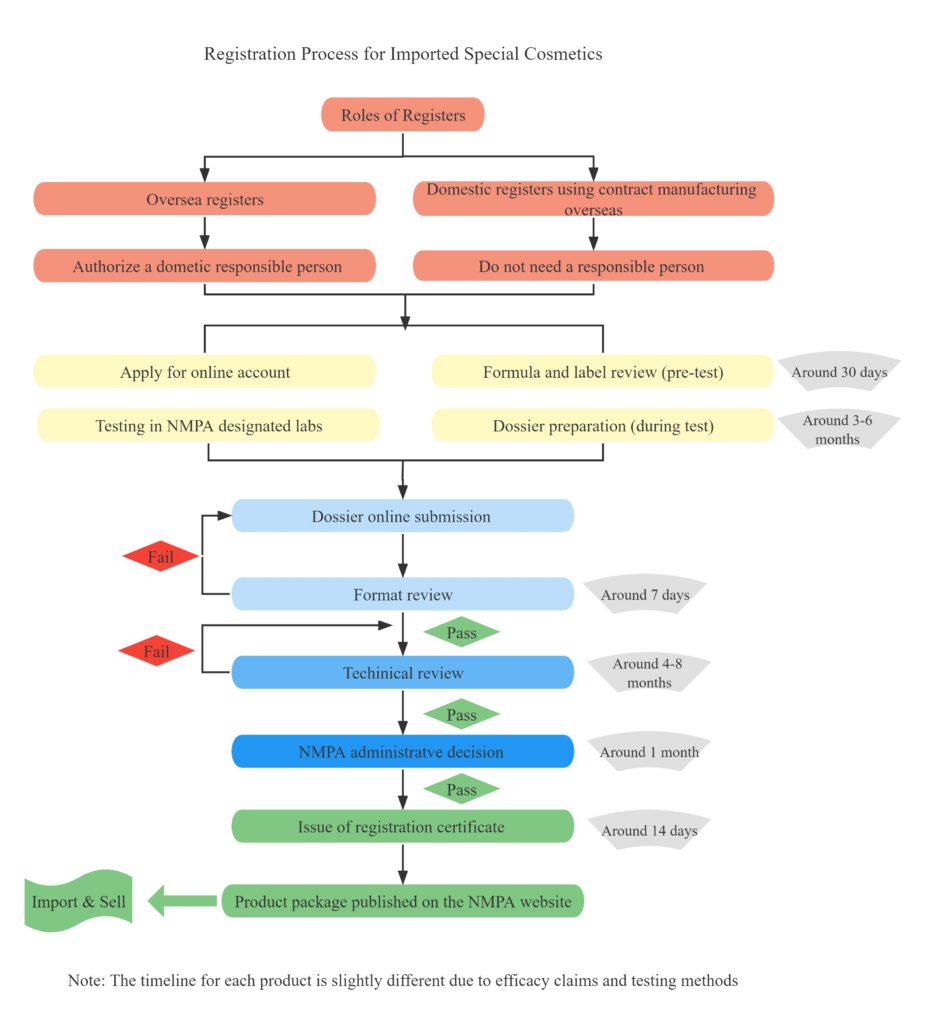
What is the timeline and procedures for registration and notification of cosmetics in China?
Normally it takes around 4-6 months for the notification of general cosmetics, and around 12-16 months for the registration of special cosmetics. As for the regulatory procedure, please refer to Table 2 Notification Process of General Cosmetics, and Table 3 Registration Process of Special Cosmetics.
Table 4 – Notification Process of General Cosmetics
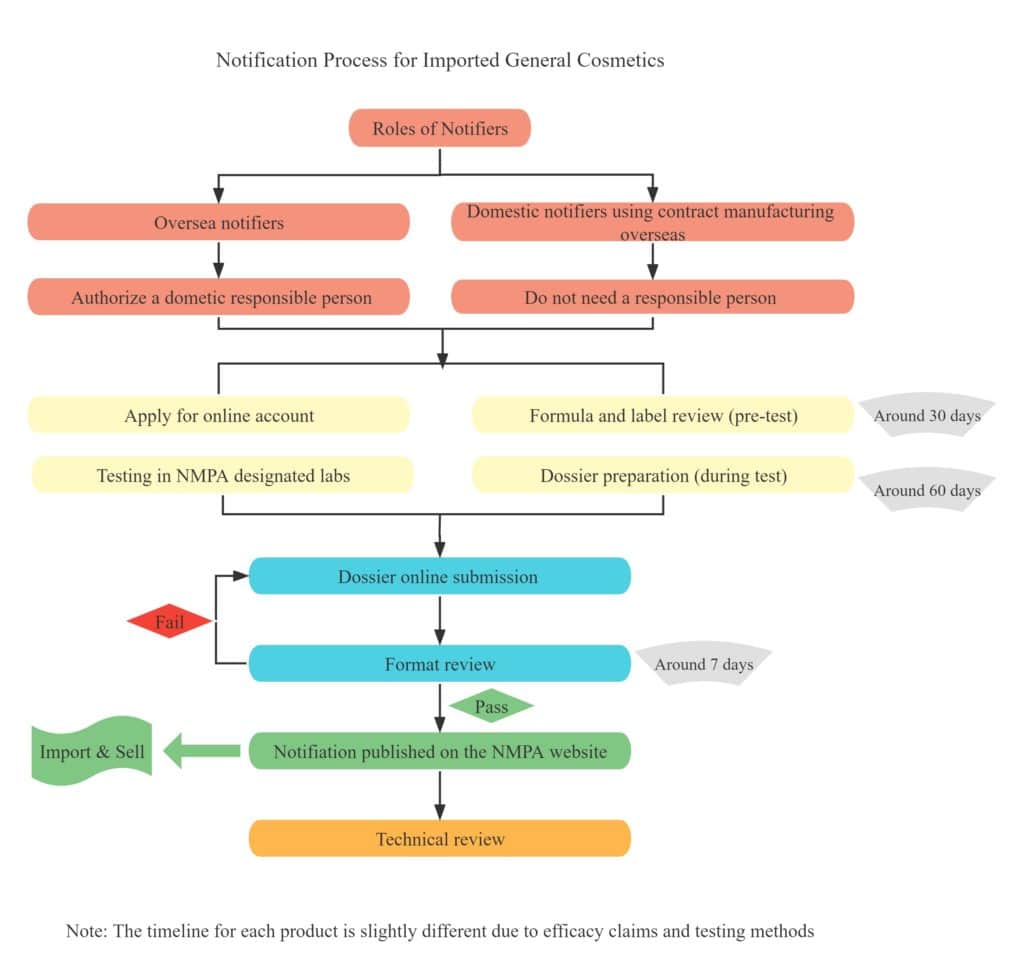
Table 5 – Registration Process of General Cosmetics
If you’re considering exporting cosmetic products to the EU market, it’s vital to have a solid understanding of the key aspects involved in placing cosmetics in the EU. This article Importing Cosmetics from China into the EU: A Guide will provide you with the necessary information to ensure a successful export.
This article is the result of a collaboration between Anaïs Thys of Taobé Consulting and Yingying Pan of ZMUni.
Navigating the regulations for cosmetics in China can be a complex and daunting task. With so many rules and requirements to follow, it can be difficult to ensure that your products are fully compliant. However, with our expert guidance and support, you can rest assured that your cosmetics will meet all necessary regulations and standards.
ZMUni has a team of experienced professionals well-versed in the intricacies of Chinese cosmetics regulations, so we can help you navigate the process with ease. From registration and notification to labeling and packaging, we have the knowledge and expertise to ensure that your products are fully compliant and ready for the Chinese market. So if you’re looking to expand your cosmetics business in China, let us help you achieve success by ensuring that your products meet all necessary regulations and standards.



